While ankle spondylosis and arthritis are often overshadowed by their more notorious counterparts like knee and hip arthritis, the depth and breadth of research in these areas are surprisingly rich and enlightening. You’ll find that the latest reviews not only dissect the complexities of these debilitating conditions but also offer hope through innovative treatment strategies. These insights can dramatically shift your understanding and approach to managing ankle joint health. Curious about how these findings might impact patient care and treatment outcomes? Let’s explore what experts are saying and consider the implications for future therapeutic developments.
Overview of Arthritis and Spondylosis
You’ll find that arthritis encompasses a range of joint disorders characterized by inflammation, while spondylosis specifically refers to the degenerative changes in the spine, including the joints and discs.
Exploring the pathophysiology of ankle spondylosis reveals how these degenerative processes affect mobility and pain levels.
Accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment options are essential for managing symptoms effectively and improving your quality of life.
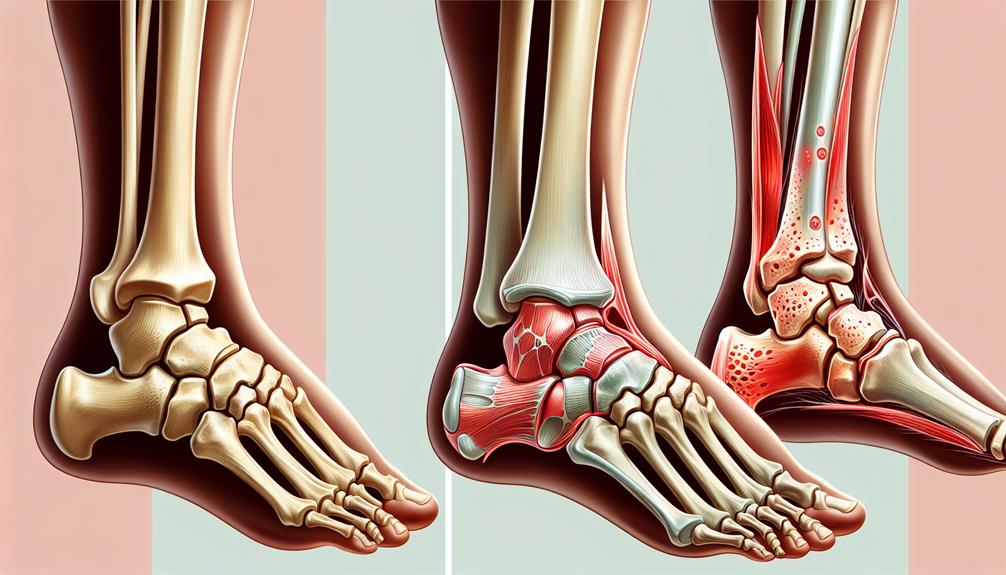
Arthritis
You must understand that arthritis in the ankle manifests in various forms, each with distinct pathological mechanisms and clinical implications.
Osteoarthritis, for instance, results from the degeneration of cartilage and is characterized by joint pain and stiffness.
Conversely, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that leads to inflammation and can cause significant joint damage if not adequately managed.
Types of Arthritis and Their Impact
Arthritis encompasses a range of joint disorders characterized by inflammation, which greatly impacts mobility and quality of life.
You’ll find osteoarthritis involves cartilage degradation, leading to bone grinding.
Conversely, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition causing joint lining inflammation.
Each type progresses distinctly and necessitates targeted interventions.
Understanding these differences is essential for effective management and potentially mitigating the debilitating effects of these conditions.
Exploring Spondylosis
You’ll find that the etiology of ankle spondylosis typically involves degenerative changes in the ankle joint, leading to gradual deterioration of articular cartilage.
Symptoms often manifest as persistent pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion, which may worsen with activity.
It’s important to recognize these signs early to manage the condition effectively and mitigate progressive joint damage.
Causes and Symptoms of Ankle Spondylosis
Ankle spondylosis, a type of osteoarthritis, develops when chronic wear and tear on the ankle joints leads to degenerative changes.
You’ll likely experience stiffness, pain, and reduced mobility. These symptoms worsen with activity but can improve with rest. It’s important to recognize early signs to manage the condition effectively.
Risk factors include aging, previous injuries, and excessive strain from activities like running or jumping.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Ankle Spondylosis
Understanding the diagnostic processes and treatment options for ankle spondylosis requires a familiarity with both the clinical symptoms and underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. Initially, your clinician will perform a detailed physical examination, focusing on your ankle’s range of motion, alignment, and any signs of deformity or swelling. They’ll likely inquire about your pain’s nature, duration, and any activities that exacerbate your symptoms.
Imaging studies play an essential role in confirming the diagnosis. Standard radiographs (X-rays) are typically the first step to visualize joint space narrowing, osteophytes, or subchondral sclerosis. For more detailed assessment, MRI or CT scans may be recommended to evaluate soft tissue involvement and cartilage deterioration.
Treatment strategies are tailored based on the severity of your condition. Conservative approaches include physical therapy to enhance joint mobility and reduce pain, alongside nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for managing inflammation.
If your symptoms persist or worsen, more invasive options like corticosteroid injections or surgery, such as arthroscopy or arthrodesis, might be considered. The choice of surgical intervention depends on your specific pathological findings and overall health status, aiming to alleviate pain and improve functional outcomes.
Reviewing Ankylosing Spondylitis
As you explore Ankylosing Spondylitis, it’s essential to understand its pathophysiology and the genetic markers associated with increased disease susceptibility.
You’ll find that current treatments focus primarily on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression through a combination of pharmacologic therapies and physical rehabilitation.
Reviewing management strategies, evidence supports a multidisciplinary approach tailored to individual patient needs to optimize function and quality of life.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Detailed Overview
You must consider the genetic predispositions when evaluating the risk factors for Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS).
Studies have shown that the presence of the HLA-B27 gene greatly increases your risk of developing AS, though it’s not the sole indicator.
Additionally, familial aggregation suggests a hereditary component, necessitating a detailed family medical history to assess your susceptibility.
Genetics and Risk Factors Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Genetic predispositions play an essential role in the development of ankylosing spondylitis, with HLA-B27 being a significant genetic marker associated with increased disease risk. You’re more susceptible if you’ve inherited this gene.
However, not everyone with HLA-B27 develops the condition, indicating other genetic and environmental factors also influence disease onset.
It’s important to take into account family history and conduct genetic testing if you’re experiencing symptoms.
Current Treatments and Management Strategies
You’ll find that managing Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) effectively involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Anti-inflammatory drugs and TNF inhibitors are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage pain, while physical therapy focuses on maintaining joint flexibility and posture.
Additionally, lifestyle adjustments, such as regular exercise and smoking cessation, play an essential role in alleviating symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Medication, Physical Therapy, and Lifestyle Changes
Current treatments for ankylosing spondylitis encompass a multifaceted approach. This includes medication, physical therapy, and strategic lifestyle adjustments to manage symptoms effectively.
You’ll typically be prescribed NSAIDs to reduce inflammation, while TNF inhibitors may be recommended for severe cases.
Regular physical therapy can improve mobility. Incorporating low-impact exercise, such as swimming, and maintaining good posture are essential to mitigating symptom progression and enhancing quality of life.
Analyzing Arthritis Review Articles
As you examine the recent arthritis review articles, you’ll notice a trend in the key findings highlighting the progression and management of ankle spondylosis.
These articles underscore the challenges faced in current research methodologies and emphasize the urgent need for innovative approaches.
Key Findings from Recent Arthritis Review Articles
As you explore recent arthritis research, you’ll notice the substantial influence these studies have on enhancing clinical practice. Current reviews underscore the necessity for integrating novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches that are directly supported by empirical data.
This shift not only improves patient outcomes but also streamlines the management protocols for ankle spondylosis and arthritis.
Impact of Arthritis Research on Clinical Practice
Recent arthritis research has greatly enhanced clinical practices by providing evidence-based strategies for improved patient outcomes.
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on genetic markers.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
- Novel Therapeutics: Introduction of biologic agents reducing inflammation and halting disease progression.
- Multidisciplinary Approaches: Integrating physical therapy and nutritional counseling into patient care plans.
Challenges and Future Directions in Arthritis Research
Arthritis research faces important challenges, including the need for more precise biomarkers and targeted therapies. As you explore further into the literature, you’ll notice the substantial gap in understanding the molecular pathways that drive different forms of arthritis. This deficiency hampers the development of specific diagnostic tools and effective treatments. It’s essential that you recognize the complexity of immune system interactions involved in arthritis, which complicates the identification of unique biomarkers.
Current therapies often offer broad immunosuppression, which isn’t ideal. You’d benefit from therapies that target specific molecular pathways with minimal side effects. The integration of systems biology and bioinformatics could propel the identification of novel therapeutic targets. However, translating these findings into clinical practice remains a slow process, fraught with regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive validation.
Looking ahead, advancements in genomics and proteomics offer promising avenues for uncovering new biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Your understanding of these technologies will be vital. Additionally, the rise of personalized medicine holds potential to tailor treatments to individual genetic profiles, potentially improving patient outcomes. You’re at the frontier of a shift towards precision medicine in treating arthritis, where your research could significantly impact future therapeutic strategies.
Exploring Ankle Spondylosis Articles
As you explore the literature on ankle spondylosis, you’ll find a robust array of studies that provide insight into its pathophysiology and management.
Recent trends in research highlight innovative treatment modalities and their efficacy, as evidenced by randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses.
It’s essential to integrate these findings into clinical practice to enhance patient outcomes in managing this degenerative condition.
Literature Review on Ankle Spondylosis
You’ll find that a comparative analysis of different ankle spondylosis studies highlights varying methodologies and outcomes.
By examining these distinctions, you can ascertain the most effective diagnostic and treatment strategies.
This approach guarantees your understanding is grounded in robust, evidence-based research.
Comparative Analysis of Different Ankle Spondylosis Studies
Several studies have systematically compared the efficacy of different treatments for ankle spondylosis, highlighting varied outcomes and methodologies.
- Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Approaches:
Evidence indicates surgical interventions may offer longer-term relief.
- Physical Therapy Modalities:
Studies show variability in patient response.
- Pharmacological Treatments:
Efficacy of NSAIDs and corticosteroids has been widely documented.
- Alternative Therapies:
Limited data suggest potential benefits but require further investigation.
Emerging Trends in Ankle Spondylosis Research
Researchers are continuously uncovering new insights into the pathophysiology and management of ankle spondylosis. You’ll find that recent studies emphasize the role of biomechanical factors in the progression of this degenerative condition. Advanced imaging techniques, such as weight-bearing MRI, are now critical in diagnosing subtle changes in the joint that aren’t apparent in traditional scans. This allows for earlier intervention, which can notably alter the disease course.
Molecular biology is also proving instrumental in understanding the inflammatory processes that contribute to spondylosis. Research indicates that cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases play pivotal roles in cartilage degradation. New therapeutic targets are being identified, focusing on these molecules to halt or even reverse the degenerative changes.
Furthermore, minimally invasive surgical techniques are advancing. These procedures aim to preserve joint mobility while reducing recovery times and post-operative complications. Techniques such as arthroscopic debridement and osteophyte removal are refined to achieve better outcomes with less impact on your daily life.
You’re also seeing a rise in the integration of regenerative medicine approaches, including stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments, which show promise in regenerating damaged tissues and slowing the progression of spondylosis. These emerging trends are reshaping how ankle spondylosis is approached, offering hope for more effective and personalized treatments.